The Ultimate Revelation Of Computer Basics

Basic System Components of a Computer*
| 1 | Motherboard—-this is the core of the system |
| 2 | Processor–this is the ‘engine’ of computer |
| 3 | Memory (RAM)–this is the primary memory |
| 4 | Case/chassis–this is the case of the computer |
| 5 | Power supply-powers the computer |
| 6 | Floppy drive–for removable media |
| 7 | Hard drive—–holds memory and programs |
| 8 | CD-ROM/DVD-ROM—for removable media optical drives |
| 9 | Keyboard—-allows you to communicate with computer |
| 10 | Mouse—-is a pointing devise to communicate with computer |
| 11 | Video card—-controls monitor color, clarity, speed |
| 12 | Monitor—is the TV of the computer |
| 13 | Sound card—controls the speakers and sound |
| 14 | Modem—connects you to internet |
PC Basics:
Equipment
A PC is comprised of numerous parts that send, get or measure data. All
PCs incorporate the accompanying equipment:
PC case: The case that holds all the electronic parts of the PC,
counting the hard plate, RAM chips, focal preparing unit (CPU), and
motherboard. Inside the case is the place all that happens.

Monitor: Similar to a TV, the screen shows text, pictures,
furthermore, different things from the PC on a screen.
Console: The arrangement of typewriter-like keys you use
to type data into the PC.

Mouse: The gadget that controls the development of the pointer showed on the screen. You utilize the mouse pointer to choose and open things on the PC.
Drives: Devices that read information from and compose information to a circle. A DVD drive peruses the two CDs and DVDs. A DVD drive has the words reduced circle on the front. Some more seasoned PCs have a drive for a diskette.
All PCs have a USB port either on the front or back of the PC case. This port is where you plug in a USB drive/thumb drive. A USB drive, floppy circle, and certain CDs are all approaches to spare records, for example, letters, pictures, and introductions.
PCs: PCs are convenient PCs with the electronic segment, screen, console and mouse all encased in a lightweight, battery-controlled, convenient unit which can fit on your lap. They are moreover now and again alluded to as „notebooks.‟
Compact Storage Devices
There will be times when you need to spare a record – either as a reinforcement, or on the grounds that you have to access the record, however will utilize an alternate PC. There are a few alternatives for sparing records:
Floppy Drive (1.44 Megabytes)
Has a modest quantity of room (around 20 records/100 pages of text)

Compact discs (700 Megabytes)
Has more space (500 fold the amount of room as a floppy plate)
DVDs (4.7 Gigabytes)
1,000 Megabytes = 1 Gigabyte

USB Drive (Universal Serial Bus) (2, 4, 8 or 16 Gigabytes)

Utilizing the Mouse
Getting open to utilizing the mouse is basic for starting PC clients. While it might appear to be somewhat abnormal from the start, moving the mouse will before long get instinctive with a little practice.
Portions of the Mouse: At the head of the mouse, there are two significant catches: the left catch and the correct catch. (A few mice additionally have a little roller which can likewise be utilized as a catch however by and large not.) Remember: the catches on the mouse ought to consistently be pointing ceaselessly from you!
Holding the Mouse:
With the catches on the mouse pointing endlessly from you, hold the sides of the mouse with your thumb, ring finger and pinkie.
Spot your forefinger on the left catch and your center finger on the correct catch.
Lay your wrist on the work area or mouse cushion.
The mouse remains on the mouse cushion. You can lift the mouse to move it when you run out of room on the cushion.
Pointing and Clicking: The most widely recognized mouse activity is pointing and clicking. Essentially move the mouse with the goal that the cursor is highlighting the article you need to choose, and afterward click the left mouse button once. Pointing and clicking is a compelling method to choose menu things, indexes, and records.
Double tapping: If you‟re utilizing a Windows Operating System, you‟ll need to double tap an thing to open projects or documents. This includes pointing at something onscreen with the cursor and at that point tapping the left mouse button twice in fast progression. For instance, to open projects,
Right-Clicking: When you select a thing and afterward click the correct mouse button, you‟ll frequently observe a spring up menu. This menu, when accessible, contains orders that legitimately identify with the chosen object. This is some of the time alluded to as an alternate way menu. Allude to your person projects to see whether and how they utilize the correct mouse button.

Relocating: Dragging is a variety of clicking. To drag an item, point at it with the cursor and afterward press and hold down the left mouse button. Move the mouse without delivering the mouse catch, and drag the item to another area. When you‟re done moving the object, discharge the mouse catch to drop it onto the new area.
Floating: When you position the cursor over a thing without clicking your mouse, youre floating over that thing. In some Microsoft programs you can float over a symbol and a little mark will seem mentioning to you what move will be made by clicking that symbol.

Utilizing the Windows Operating System
The working framework on the PC is the program that begins when you turn on the PC. It plays out the essential errands needed to utilize the PC, incorporating collaborating with the PC equipment, planning errands, and looking after documents. The working framework likewise deals with the other programs on the PC. In the event that you are utilizing a PC, you will presumably have one of the accompanying working frameworks: Windows 7 or Windows 10. PCs utilizing a Microsoft Windows working framework have the accompanying highlights:
The work area: When you first sign on to the PC, you see the work area. The work area is the presentation territory you see when Windows opens. The significant pieces of the Windows work area incorporate the accompanying:
Start button: The Start button is in the lower left-hand corner of your screen. In Window 7, the round Microsoft globe is the Start button. (In prior variant, the catch was marked “Start”) This catch opens the Start menu, which is the thing that you can use to open projects and archives.
Taskbar: Located along the base of the screen. Showcases catches for your open applications and windows just as symbols to open a few projects.
Framework Tray: The right-hand part of the taskbar that holds the clock, volume control, and symbols for different utilities that run in the foundation of your framework.
Alternate route symbols: These are connections to projects, document or envelopes that you can put on your work area.
Recycle: This is the place you can move any records you need to erase.
Mouse pointer: The marker on the screen that you use to choose and move objects. It moves as you move the mouse and it changes appearance relying upon what program you are utilizing and what apparatus you have chosen.
“Windows“: Using the Microsoft Windows working framework, you can have mutiple program or organizer open for survey simultaneously. Each program or organizer is in its own window, a rectangular zone on the screen. Having various windows open is like having numerous books open on the head of a work area.
Every window contains diverse data. For example, you can have a window open that shows a letter you are composing and a window that shows a guide of the world. At the point when you are utilizing different windows, the one you are working in is known as the dynamic window. The dynamic window is situated on head of different windows and is in the closer view.
Basic Windows components: Most windows have regular highlights, so once you become acquainted with one program, you can utilize that information in another program.
Title bar: The top bar of a window showing the title of the program and the name of the archive.
Menu bar: The bar containing names of menus, situated underneath the title bar. You can utilize the menus on the menu bar to get to a considerable lot of the apparatuses accessible in a program.
Toolbars: The bar underneath the menu bar containing catches that give admittance to the most ordinarily utilized instruments in a program. Each catch has an image on it, additionally called a “symbol”, which speaks to the button‟s activity.

Strips: If you are utilizing a Microsoft Office 2010 item, you don’t have menus or toolbars. Rather you have the “Lace”. Strips are gotten to by tapping on any of the tabs towards the head of the window. Contingent upon what tab you click, you can get to various Ribbons. Every lace contains an alternate gathering of symbols which performs different errands. For instance, on the Home Ribbon, you can discover symbols that will change which textual style you are utilizing or what size text style you are utilizing.
Limit button: The left catch in the upper-right corner of a window used to
limit a program window. A limited program stays open yet it is noticeable as it were as a catch on the taskbar.
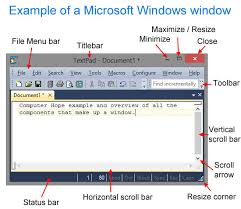
Resize button: The center catch in the upper-right corner of a window used to resize a program window. In the event that a program window is full-screen size, that is, it fills the whole screen, the Restore Down catch is shown. You can utilize the Restore Down catch to decrease the size of a program window. In the event that a program window is not exactly full-screen size, the Maximize button is shown. You can utilize the Maximize catch to amplify a program window to full-screen size.
Close catch: The correct catch in the upper-right corner of a window used to close a program or report window.
Parchment bars: A vertical bar on a window and a flat bar at the base of
the window used to move around in an archive. You can utilize the parchment bolts to see different pieces of the screen by “looking” here and there or left and right. In the event that the whole archive is shown in the window
I have a GREAT Course for you on Computer Basics! CLICK HERE













